
Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Energy Metabolism
Quantitative Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Bile Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Trimethylamine Oxide and Related Metabolites
Quantitative Analysis of Amino Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Neurotransmitters
Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates
Quantitative Analysis of Plant Hormones
Quantitative Analysis of Carotenoids
Quantitative Analysis of Tannins
Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Anthocyanins
Fatty Acid (Fatty Acid) is a general term for the fatty acids formed by the hydrolysis of natural oils and fats with water. At present, there are more than 200 kinds of natural fatty acids, which are widely found in animal and vegetable fats.
Fatty acids play a very important role in the course of life. They are the basic substances that make up human body fat and lipids. They are important components of cell membrane phospholipids, it can also directly regulate the composition of cell membrane and the proteins and receptors in the membrane. With the development of fat nutrition research, people pay more and more attention to the nutritional function, biological function and the relationship with disease and health of fatty acids.
Journal: Nature Common Impact factor: 12.121 Published date: August, 2020 Published by: University of Toulouse, France
Autophagy has been associated with oncogenesis with one of its emerging key functions being its contribution to the metabolism of tumors. Therefore, deciphering the mechanisms of how autophagy supports tumor cell metabolism is essential. Here, we demonstrate that the inhibition of autophagy induces an accumulation of lipid droplets (LD) due to a decrease in fatty acid β-oxidation, that leads to a reduction of oxidative phosphorylation (OxPHOS) in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), but not in normal cells. Thus, the autophagic process participates in lipid catabolism that supports OxPHOS in AML cells. Interestingly, the inhibition of OxPHOS leads to LD accumulation with the concomitant inhibition of autophagy. Mechanistically, we show that the disruption of mitochondria–endoplasmic reticulum (ER) contact sites (MERCs) phenocopies OxPHOS inhibition.
Altogether, our data establish that mitochondria, through the regulation of MERCs, controls autophagy that, in turn finely tunes lipid degradation to fuel OxPHOS supporting proliferation and growth in leukemia.
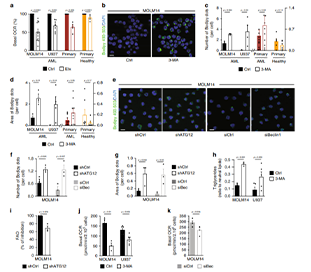 Autophagy participation in lipid decomposition contributes to OxPHOS
Autophagy participation in lipid decomposition contributes to OxPHOS
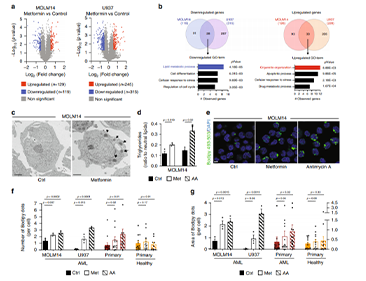 Inhibition of OxPHOS affects lipid metabolism
Inhibition of OxPHOS affects lipid metabolism
This study establishes a model of the bidirectional relationship between autophagy and mitochondrial metabolism, confirming the notion that lipid transfer proteins may be located in MERCs.
Bosc Claudie,Broin Nicolas,Fanjul Marjorie et al. Autophagy regulates fatty acid availability for oxidative phosphorylation through mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum contact sites.[J] .Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 4056
 © Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd