
Ionomics is an emerging discipline that studies the composition, distribution and accumulation of elements in the body, as well as the changes and mechanisms of these elements in random body physiological conditions, biological and abiotic stimuli, developmental stages, environment and genetics. All metals, metalloids and non-metals. Ionic elements are widely involved in various important life activities and perform important physiological functions.
Genetic Basis of Rice Ionomic Variation Revealed by Genome-Wide Association Studies
Journal: The Plant Cell Impact factor: 8.631 Published date: October, 2018
Published by: Huazhong Agricultural University, National Plant Genetic Research Center
Rice (Oryza sativa) is an important dietary source of both essential micronutrients and toxic trace elements for humans. The genetic basis of mineral composition (ion) variation in rice remains largely unknown.
Using genome-wide association studies (GWAS), the research team measured the content of 17 mineral elements in straw and grains using 529 samples of rice from fields in Hubei and Hunan over several years, the genetic basis of rice ion group natural variation was analyzed by association analysis with single base sequence polymorphism information of rice genome.
32 loci were detected repeatedly in different sites, and 40 loci were detected repeatedly in different field trials at the same site. The candidate genes of 42 loci, including OSHKT1; 5, OSMOT1; 1 and Ghd7, were predicted, this study provided available genetic loci and theoretical basis for genetic improvement of rice nutrition quality.
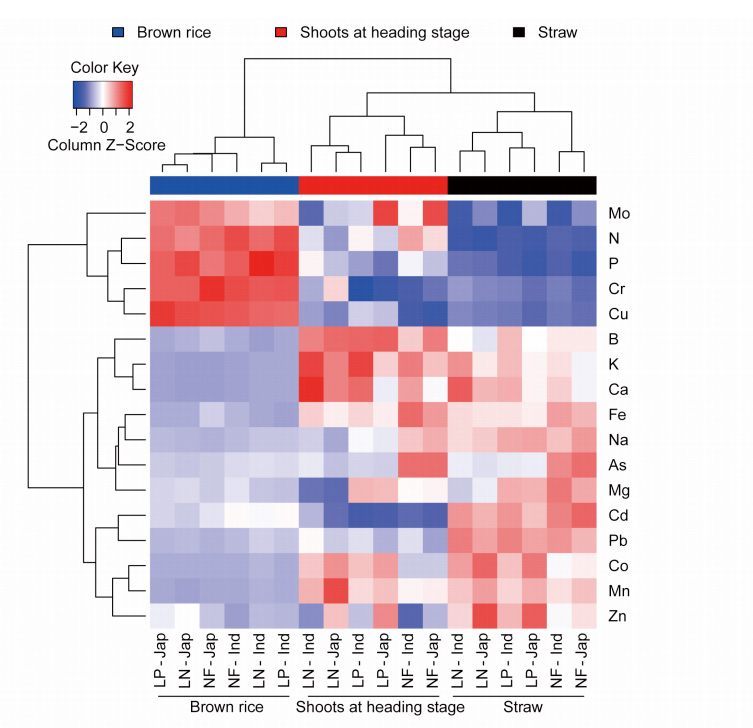 Figure 1 Based on the cluster analysis of rice natural population, the cluster analysis of the main components including field conditions, sub-groups and tissues was carried out by using the concentration of each element
Figure 1 Based on the cluster analysis of rice natural population, the cluster analysis of the main components including field conditions, sub-groups and tissues was carried out by using the concentration of each element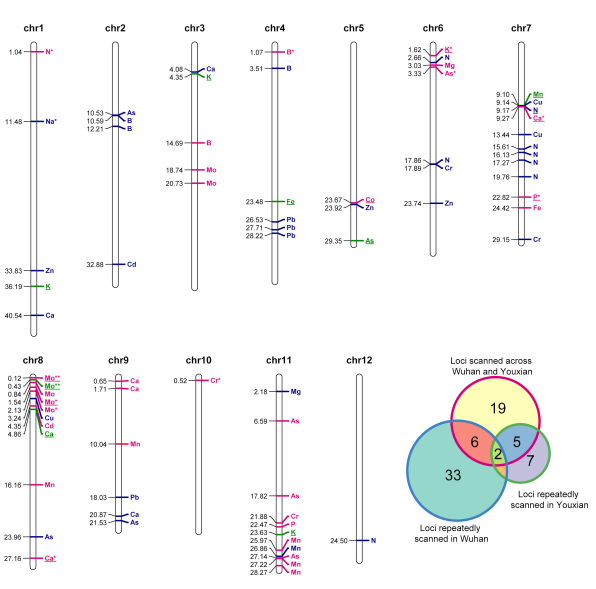 Figure 2 Distribution of 72 common loci scanned repeatedly on 12 chromosomes according to physical distance
Figure 2 Distribution of 72 common loci scanned repeatedly on 12 chromosomes according to physical distance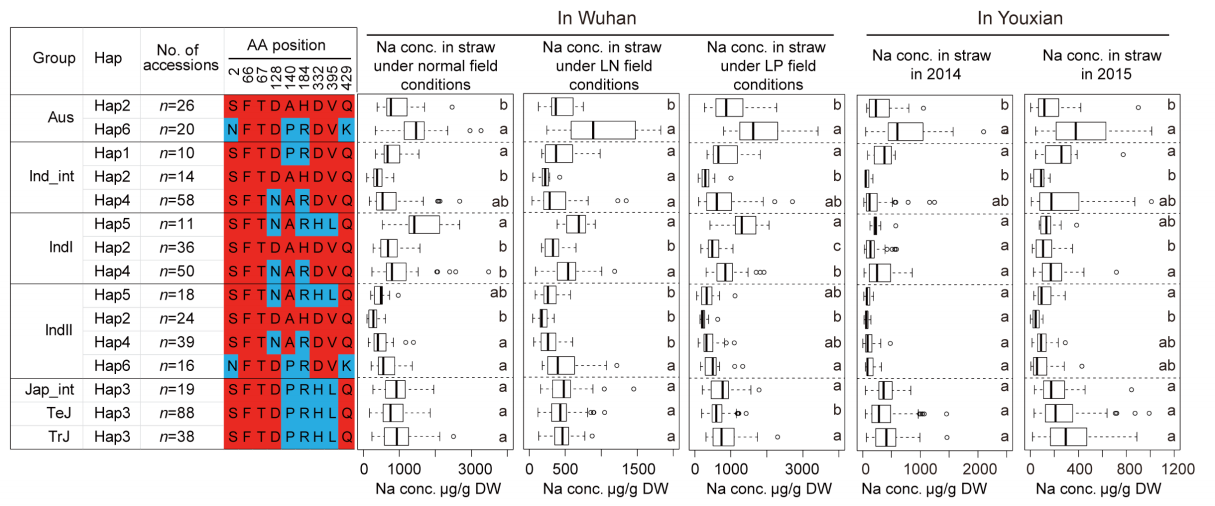 Figure 3 Analysis of Na concentration in different Os-HKT1:5 haplotypes. The letters on the color background are one-letter codes for the corresponding amino acid residues. The same and different amino acid residues in HAP2 are shown in red and blue
Figure 3 Analysis of Na concentration in different Os-HKT1:5 haplotypes. The letters on the color background are one-letter codes for the corresponding amino acid residues. The same and different amino acid residues in HAP2 are shown in red and blue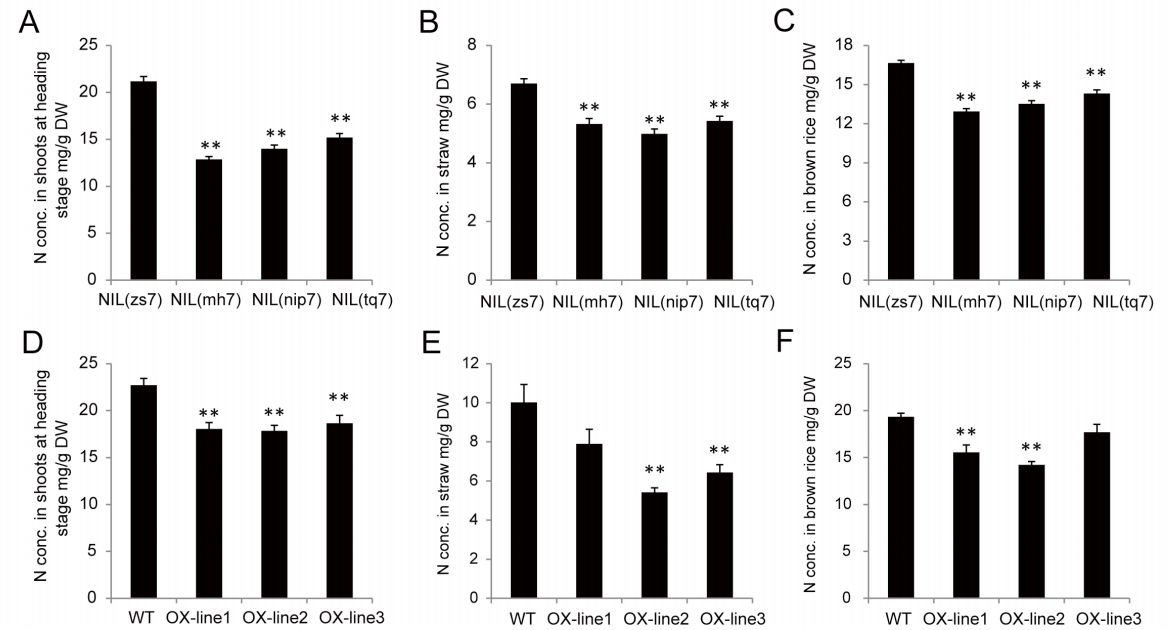 Figure 4 Based on near-isogenic lines and transgenic plants, the role of Ghd7 in nitrogen accumulation in rice was analyzed
Figure 4 Based on near-isogenic lines and transgenic plants, the role of Ghd7 in nitrogen accumulation in rice was analyzedA comprehensive study on the genetic structure of rice ion variation will help to reveal the regulatory mechanism of mineral nutrition and microelement composition in plants.
Yang M , Lu K , Zhao F J , et al. Genetic basis of rice ionomic variation revealed by Genome-wide association studies[J]. The Plant Cell, 2018, 30
 © Copyright 2015-2025 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2025 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd