
Quantitative Analysis of Anthocyanins
Quantitative Analysis of Energy Metabolism
Quantitative Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Bile Acids
uantitative Analysis of Trimethylamine Oxide and Related Metabolites
Quantitative Analysis of Amino Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Neurotransmitters
Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates
Quantitative Analysis of Plant Hormones
Quantitative Analysis of Carotenoids
Quantitative Analysis of Tannins
Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Anthocyanins
Anthocyanins, are a class of water-soluble natural pigments that are widely found in plants. Most of the main color substances in fruits, vegetables and flowers are related to it. Absolute quantification of anthocyanins, analysis of quercetin, rutin, mallow pigment, etc.absolute qualitative and quantitative , and the analysis results are true and reliable. The relative quantification of anthocyanins can simultaneously conduct quantitative analysis and detection of hundreds of anthocyanins in plants, such as rutin, cyanidin, coumarin, etc.
Journal: Nature Communications Impact factor: 12.121 Published date: May, 2020 Published by: Michigan State University, the United States
Anthocyanin pigments furnish a powerful visual output of the stress and metabolic status of Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Essential for pigment accumulation is TRANSPARENT TESTA19(TT19), a glutathione S-transferase proposed to bind and stabilize anthocyanins, participating in their vacuolar sequestration, a function conserved across the flowering plants.
Identification of genetic suppressors that result in anthocyanin accumulation in the absence of TT19.
mutations in RDR6, SGS3, or DCL4 suppress the anthocyanin defect of tt19 by pushing carbon towards flavonoid biosynthesis.
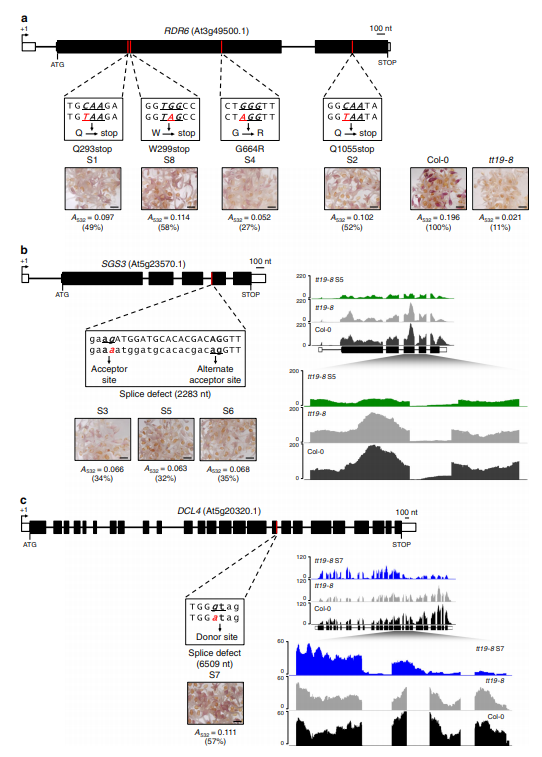 Figure 1 Molecular characterization of the tt19-8 phenotypic suppressors S1-S8 and corresponding anthocyanin accumulation
Figure 1 Molecular characterization of the tt19-8 phenotypic suppressors S1-S8 and corresponding anthocyanin accumulation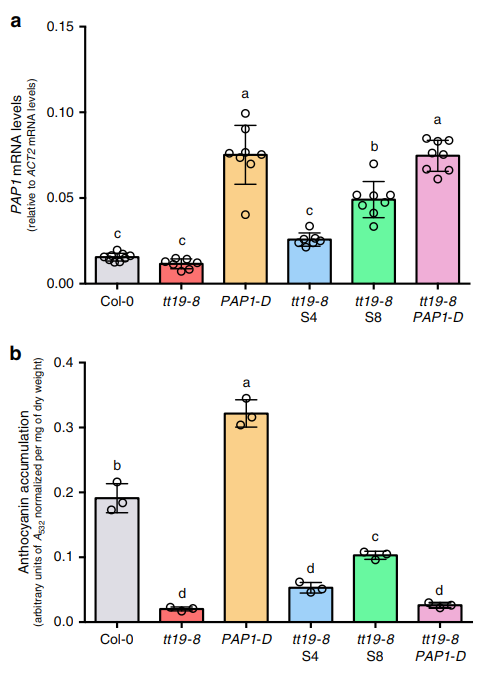 Figure 2 Over-expression of PAP1 is not sufficient to suppress the anthocyanin deficiency in tt19-8.
Figure 2 Over-expression of PAP1 is not sufficient to suppress the anthocyanin deficiency in tt19-8.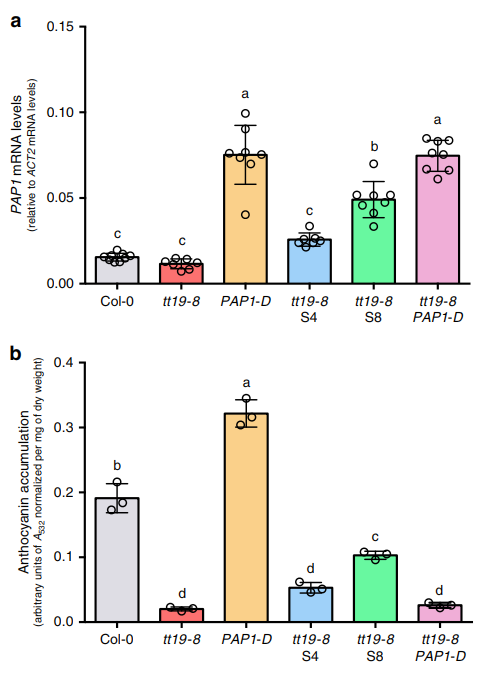 Figure 3 Flavonoids from COL-0 and Arabidopsis mutant plantlet grown in AIC. Use LC-MS/MS to compare a set of real known
Figure 3 Flavonoids from COL-0 and Arabidopsis mutant plantlet grown in AIC. Use LC-MS/MS to compare a set of real knownMutations in RDR6, SGS3, or DCL4 suppress the anthocyanin defect of tt19 by pushing carbon towards flavonoid biosynthesis. This effect is not unique to tt19 and extends to at least one other anthocyanin pathway gene mutant. This synergy between mutations in components of the RDR6-SGS3-DCL4 siRNA system and the flavonoid pathway reveals genetic/epigenetic mechanisms regulating metabolic fluxes.
Jiang Nan,Gutierrez-Diaz Aimer,Mukundi Eric et al. Synergy between the anthocyanin and RDR6/SGS3/DCL4 siRNA pathways expose hidden features of Arabidopsis carbon metabolism.[J] .Nat Commun, 2020, 11: 2456
 © Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd