
Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
Quantitative Analysis of Energy Metabolism
Quantitative Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Bile Acids
uantitative Analysis of Trimethylamine Oxide and Related Metabolites
Quantitative Analysis of Amino Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Neurotransmitters
Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates
Quantitative Analysis of Plant Hormones
Quantitative Analysis of Carotenoids
Quantitative Analysis of Tannins
Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Anthocyanins
Flavonoids is a general term for a class of compounds with a chromone ring and a benzene ring as the basic structures. There are some secondary metabolites produced by plants in the long-term natural selection . It has a variety of important physiological and biochemical effects, and has important prevention and treatment value for human diseases, such as anti-tumor effect, anti-cardiovascular disease, anti-osteoporosis, elimination of free radicals, antioxidant and anti-aging effects, bacteriostatic and anti-viral effects. , immune regulation, anti-radiation and so on. The pharmacological activity and low toxicity of broad-spectrum have made it a research hotspot at home and abroad, especially in the fields of development and utilization of medicine, food, and health care.
Journal: Food Chemistry Impact factor: 6.306 Published date: December, 2019 Published by: Institute of Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry
Olive (Olea europaea) is a rich source of valuable bioactive polyphenols, which has attracted widespread interest.
In this study, we combined targeted metabolome, Pacbio ISOseq transcriptome, and Illumina RNA-seq transcriptome to investigate the association between polyphenols and gene expression in the developing olive fruits and leaves. A total of 12 main polyphenols were measured, and 122 transcripts of 17 gene families, 101 transcripts of 9 gene families, and 106 transcripts of 6 gene families that encode for enzymes involved in flavonoid, oleuropein, and hydroxytyrosol biosynthesis were separately identified. Additionally, 232 alternative splicing events of 18 genes related to polyphenol synthesis were analyzed. This is the first time that the third generations of full-length transcriptome technology were used to study the gene expression pattern of olive fruits and leaves. The results of transcriptome combined with targeted metabolome can help us better understand the polyphenol biosynthesis pathways in the olive.
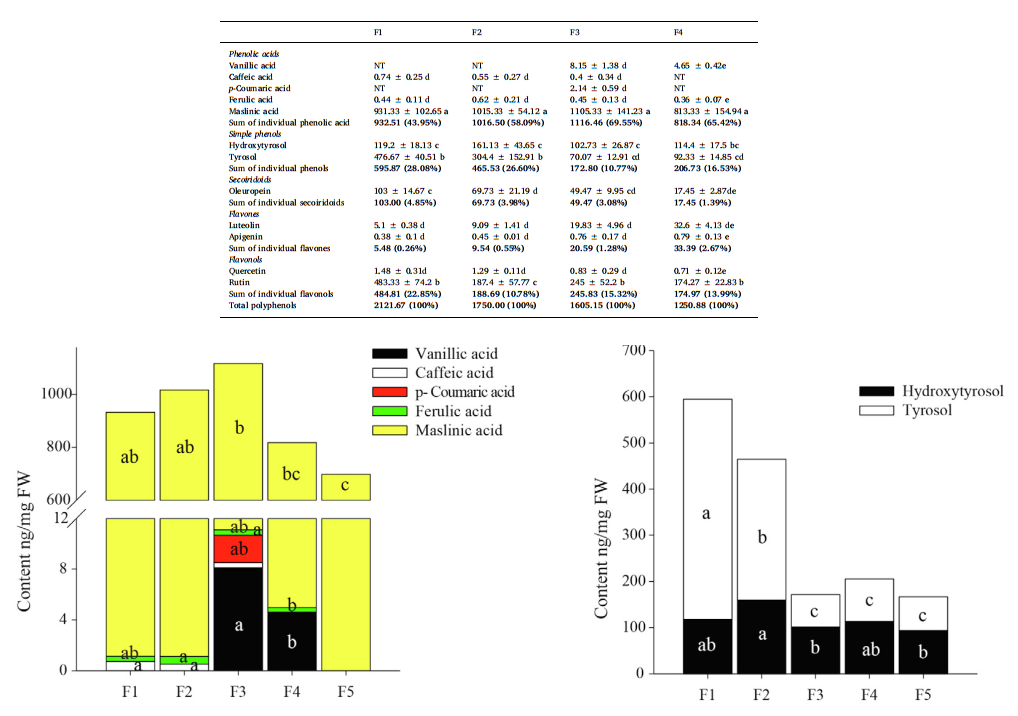 Content analysis of polyphenols,Polyphenols in 5 different stages of olive fruit development and 3 different ages of olive leaves were determined. The sum of 12 monomer polyphenols in all fruit and leaf samples was significantly different
Content analysis of polyphenols,Polyphenols in 5 different stages of olive fruit development and 3 different ages of olive leaves were determined. The sum of 12 monomer polyphenols in all fruit and leaf samples was significantly different
 Transcription analysis related to the synthesis of olive brass,the expression of 387 transcripts, including HCT, C3H, CSE and COMT genes, was significantly different at different developmental stages
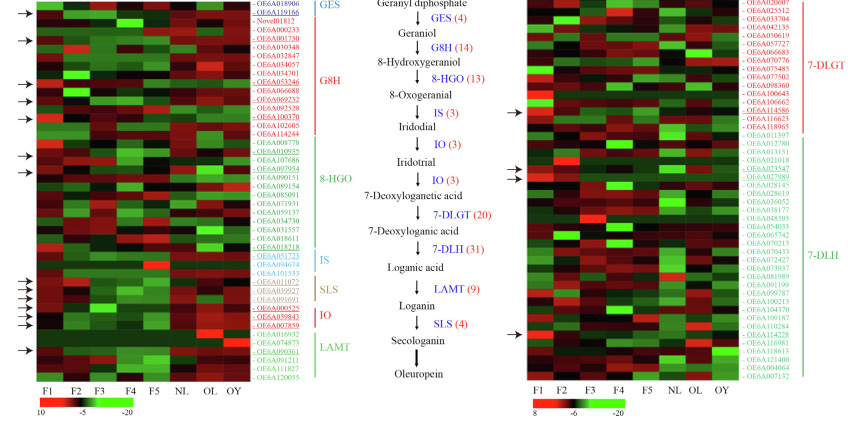
Transcription analysis related to the synthesis of olive brass,the expression of 387 transcripts, including HCT, C3H, CSE and COMT genes, was significantly different at different developmental stages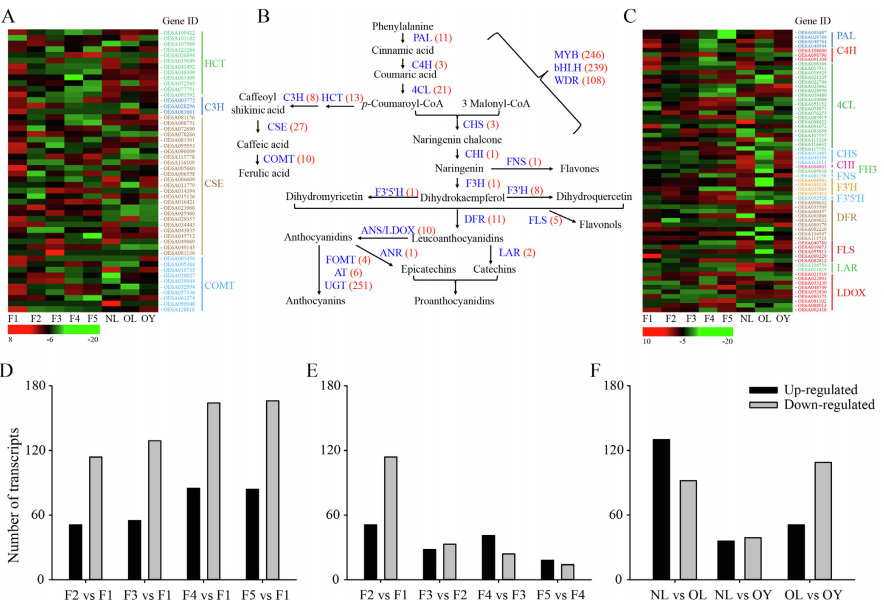 Transcriptional analysis related to oleuropein synthesis in Olive,with fruit ripening, the expression levels of GES, G8H, and other transcripts decreased, corresponding to the change of olivin concentration
Transcriptional analysis related to oleuropein synthesis in Olive,with fruit ripening, the expression levels of GES, G8H, and other transcripts decreased, corresponding to the change of olivin concentration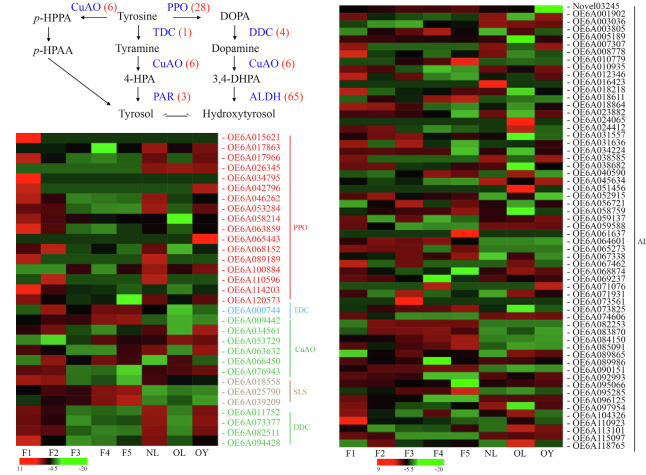 Transcript analysis related to synthesis of hydroxytyrosol from olive,Ninety transcripts related to hydroxytyrosol biosynthesis were detected, 51 of which were significantly differentially expressed in fruits and 35 in leaves
Transcript analysis related to synthesis of hydroxytyrosol from olive,Ninety transcripts related to hydroxytyrosol biosynthesis were detected, 51 of which were significantly differentially expressed in fruits and 35 in leavesThis is the first time that the third generation full-length transcriptional sequencing technology has been used to study polyphenol synthesis and related gene expression patterns in olive, which provides a valuable resource for future research on gene discovery, molecular breeding, and metabolic engineering in olive.
Guodong Rao,Jianguo Zhang,Xiaoxia Liu et al. Identification of putative genes for polyphenol biosynthesis in olive fruits and leaves using full-length transcriptome sequencing.[J] .Food Chem, 2019, 300: 125246
 © Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd