
Quantitative Analysis of Arachidonic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Energy Metabolism
Quantitative Analysis of Short-Chain Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Fatty Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Bile Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Trimethylamine Oxide and Related Metabolites
Quantitative Analysis of Amino Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Neurotransmitters
Quantitative Analysis of Organic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Flavonoids
Quantitative Analysis of Carbohydrates
Quantitative Analysis of Plant Hormones
Quantitative Analysis of Carotenoids
Quantitative Analysis of Tannins
Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Acids
Quantitative Analysis of Anthocyanins
Arachidonic acid is an 2-carbon unsaturated fatty acid. Under the action of inflammatory stimuli and mediators, it is metabolized by cyclooxygenase and lipid oxygenase pathways to generate various metabolites, mainly has prostaglandins (PG) and Leukotriene (LT). Inflammation stimulates arachidonic acid and releases its metabolites, led to inflammatory reactions such as fever, pain, vasodilation, increased permeability, and leukocyte exudation.
Journal: Ocular Surface Impact factor: 12.33 Published date: July, 2020 Published by: National University of Singapore
Trabeculectomy surgery could affect ocular surface disease (OSD) in several ways, through cessation of long term glaucoma eyedrops, exposure to operative mitomycin C and post-operative eyedrops including corticosteroids and aminoglycosides and reduction in eyelid hygiene measures. Previously we showed the relevance of tear lipid mediators (also referred oxylipins) in OSD. Here, we aim to evaluate changes of these lipids in a post-trabeculectomy cohort.
Patients undergoing trabeculectomy were prospectively evaluated and had tear collected using Schirmer’s strips, preoperatively and postoperatively at 0.5, 1.0 and 3.0 years. Lipid mediators were analyzed using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry.
The normalized concentrations of 40 lipid mediators were between 0.1-8.0 ng/mL, whereas docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), Arachidonic acid (AA) and eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) ranged up to a few hundred ng/mL. The concentrations of lipid mediators, except DHA, EPA, and thromboxane (TXB1), showed reduction after surgery.
 Figure 1 Complete and representative chromatograms of LC-MS/MS extracted tear samples and standards
Figure 1 Complete and representative chromatograms of LC-MS/MS extracted tear samples and standards 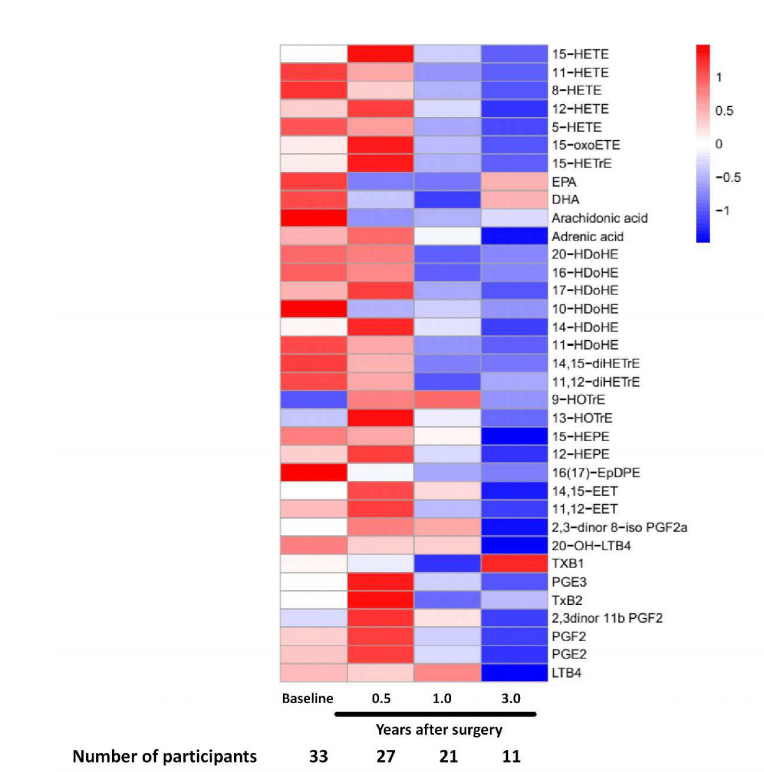 Figure 2 Heat map of postoperative lipid mediator trends over time
Figure 2 Heat map of postoperative lipid mediator trends over time Figure 3 Unsupervised hierarchical clustering heat maps
Figure 3 Unsupervised hierarchical clustering heat maps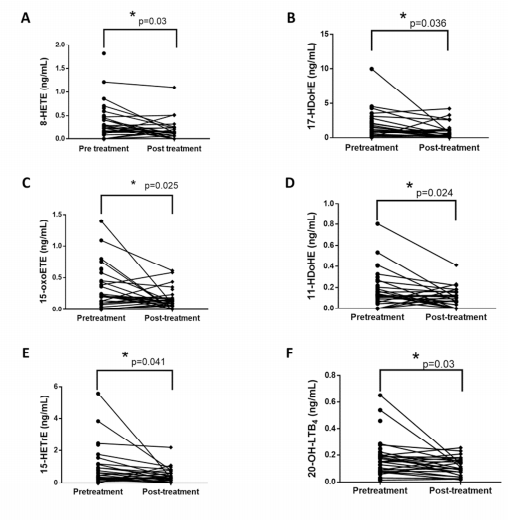 Figure 4 Effects of trabeculectomy on lipid medium levels from baseline to last recorded values
Figure 4 Effects of trabeculectomy on lipid medium levels from baseline to last recorded valuesIn this 3-years study, trabeculectomy reduced the tear level of proinflammatory lipid mediators.
Ambaw Yohannes Abere,Wong Tina,Chong Rachel et al. Change of tear lipid mediators in a post-trabeculectomy cohort.[J] .Ocul Surf, 2020
 © Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd