
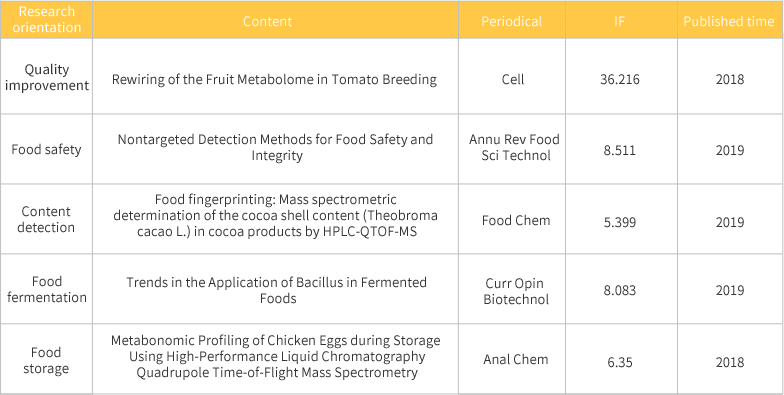
Food Quality Research
The study of food quality is an important research content in the field of food science. Food quality research includes quality identification, quality improvement, food processing, food storage and other aspects. The research of food quality depends on the means and methods of detection, which directly affect the reliability, stability and accuracy of the detection results.
Metabolomics is the qualitative and quantitative analysis of metabolites in biological samples to explore the corresponding relationships of metabolites in biological samples. Including liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and other techniques. In the field of food quality research, metabonomics method is used to analyze its mechanism. The absolute or relative content of the detected metabolites can be obtained directly. The corresponding relationship between metabolites and key time points in food fermentation process and the determination of food flavor substances were investigated.

Carbohydrates, organic acids, tannins, flavonoids, vitamins, fatty acids, amino acids, arachidonic acid...
Journal: Cell Impact factor: 38.637 Published date: 2018 Published by: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Humans heavily rely on dozens of domesticated plant species that have been further improved through intensive breeding.
To evaluate how breeding changed the tomato fruit metabolome, we have generated and analyzed a dataset encompassing genomes, transcriptomes, and metabolomes from hundreds of tomato genotypes.
The combined results illustrate how breeding globally altered fruit metabolite content. Selection for alleles of genes associated with larger fruits altered metabolite profiles as a consequence of linkage with nearby genes. Selection of five major loci reduced the accumulation of anti-nutritional steroidal glycoalkaloids in ripened fruits, rendering the fruit more edible. Breeding for pink tomatoes modified the content of over 100 metabolites. The introgression of resistance genes from wild relatives in cultivars also resulted in major and unexpected metabolic changes.
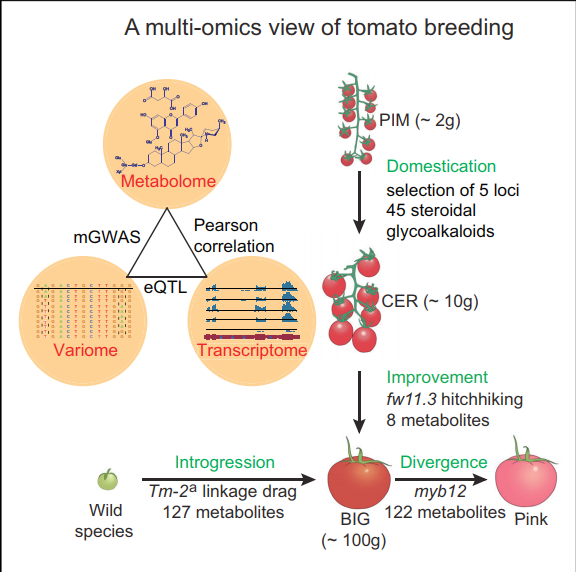 Figure 1 The view of polyomics in tomato breeding
Figure 1 The view of polyomics in tomato breeding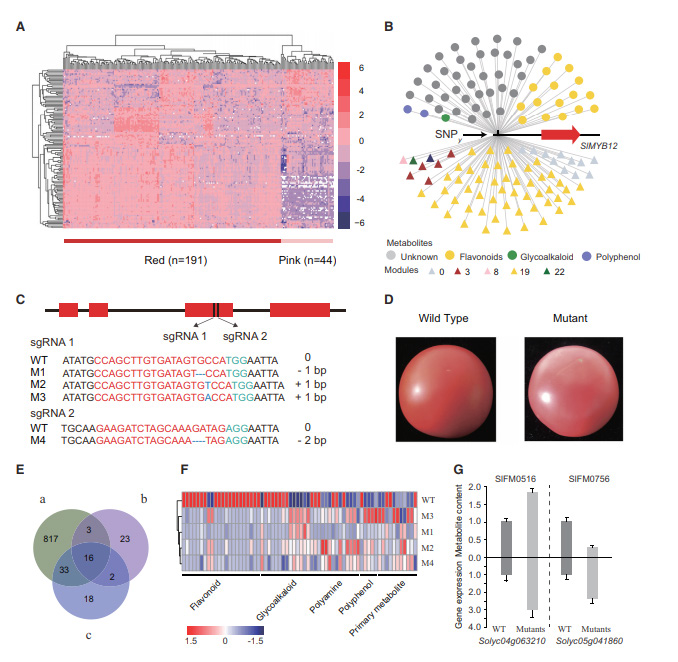 Figure 2 Metabolites and pathways affected by vitamin B12
Figure 2 Metabolites and pathways affected by vitamin B12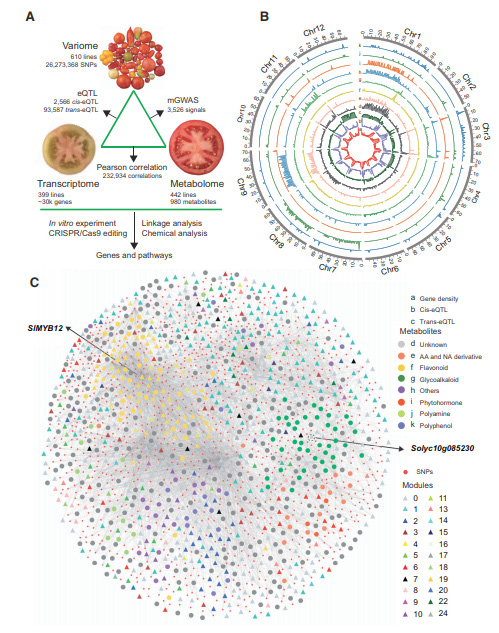 Figure 3 Generation and integration of multiple sets of data
Figure 3 Generation and integration of multiple sets of dataThe study reveals a multi-omics view of the metabolic breeding history of tomato, as well as provides insights into metabolome-assisted breeding and plant biology.
Zhu Guangtao,Wang Shouchuang,Huang Zejun et al. Rewiring of the Fruit Metabolome in Tomato Breeding.[J] .Cell, 2018, 172: 249-261.e12
 © Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd
© Copyright 2015-2022 Suzhou PANOMIX Biomedical Tech Co.,Ltd